Journal Information
Journal ID (publisher-id): BM
Journal ID (nlm-ta): Biochem Med (Zagreb)
Title: Biochemia Medica
Abbreviated Title: Biochem. Med. (Zagreb)
ISSN (print): 1330-0962
ISSN (electronic): 1846-7482
Publisher: Croatian Society of Medical Biochemistry and Laboratory Medicine
Article Information
Copyright statement: ©Croatian Society of Medical Biochemistry and Laboratory Medicine.
Copyright: 2023, Croatian Society of Medical Biochemistry
License (open-access):
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Date received: 05 December 2023
Date accepted: 24 July 2024
Publication date: 15 October 2024
Publication date: 15 October 2024
Volume: 34
Issue: 3
Electronic Location Identifier: 030705
Publisher ID: bm-34-3-030705
DOI: 10.11613/BM.2024.030705
Establishment and application of autoverification system for HbA1c testing
Xinqi Cheng[*]
Ling Qiu[*]
Author notes:
[*] Corresponding authors: chengxq@pumch.cn, lingqiubj@163.com
Author contributions
R Gao: Formal analysis, Project administration, Writing; F Zhao: Investigation, Validation; L Xia: Investigation; C Ma: Data duration, Software; Y Hu: Validation; Z Qi: Validation; L Qiu: Supervision, Funding acquisition.
• Analysis of the chromatography map of HbA1c was involved in the autoverification procedure
•Real world data was used to establish autoverification rules for HbA1c
• The optimal auto-verification system of HbA1c results was set up based on the fast plasma glucose distribution according to HbA1c groups and reference change value
Introduction
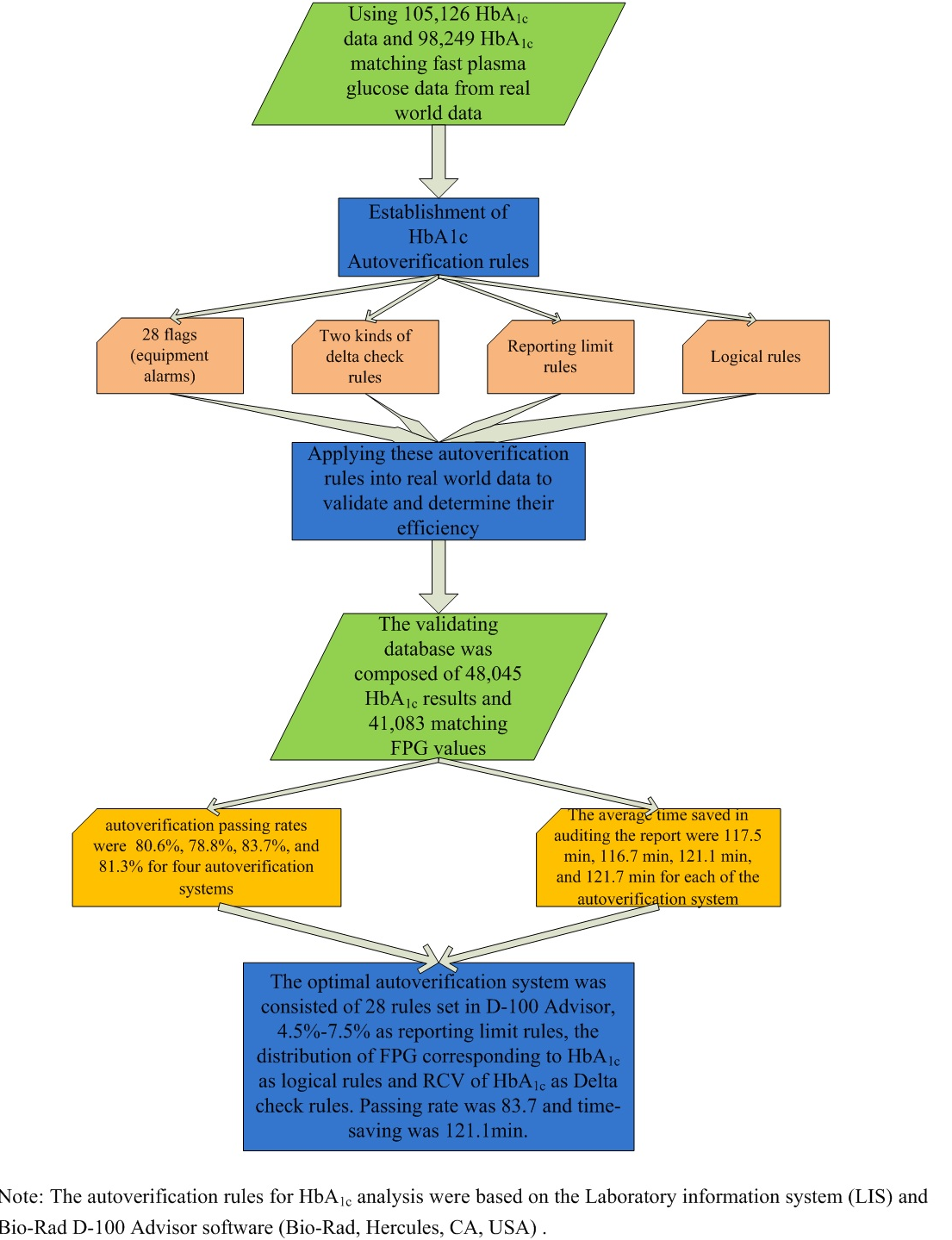
This study aimed to determine autoverification rules for routine glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) analysis based on high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) principle. Laboratory information system (LIS) and Bio-Rad D-100 Advisor software (Bio-Rad, Hercules, USA) with graphics recognition function were carriers for the autoverification system.
Materials and methods
A total of 105,126 HbA1c results, including 98,249 HbA1c matching fast plasma glucose (FPG) results of real-world data from May 2019 to June 2020, were collected to determine autoverification rules including flags, delta checks, reporting limits, and logical rules. The validation database was composed of 48,045 HbA1c results and 41,083 matching FPG results. Autoverification passing rate and the reduction of turnaround time (TAT) were evaluated.
Results
Four autoverification systems (A, B, C, D) were established by two types of delta check rules, 28 flags, one reporting limits, and two kinds of logical rules. The autoverification passing rates were 80.6%, 78.8%, 83.7%, and 81.3%, and the average time saved in TAT were 117.5 min, 116.7 min, 121.1 min, and 121.7 min, respectively.
Keywords: HbA1c; autoverification; reference change value; laboratory information system