Journal Information
Journal ID (publisher-id): BM
Journal ID (nlm-ta): Biochem Med (Zagreb)
Title: Biochemia Medica
Abbreviated Title: Biochem. Med. (Zagreb)
ISSN (print): 1330-0962
ISSN (electronic): 1846-7482
Publisher: Croatian Society of Medical Biochemistry and Laboratory Medicine
Article Information
Copyright statement: ©Croatian Society of Medical Biochemistry and Laboratory Medicine.
Copyright: 2023, Croatian Society of Medical Biochemistry
License (open-access):
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Date received: 28 January 2024
Date accepted: 12 July 2024
Publication date: 15 October 2024
Publication date: 15 October 2024
Volume: 34
Issue: 3
Electronic Location Identifier: 030502
Publisher ID: bm-34-3-030502
DOI: 10.11613/BM.2024.030502
Diagnostic role of urine human epididymis protein 4 in ovarian cancer
Antonija Hanžek[*]
Anne-Cécile E. Duc[*]
Author notes:
[*] Corresponding authors: antonija.hanzek@unimes.fr, anne-cecile.duc@unimes.fr
Author contributions
A Hanžek: Conceptualization and Methodology; A Hanžek, C Siatka, A-C E. Duc: Writing - review & editing; C Siatka, A-C E. Duc: Project administration, Management and Supervision.
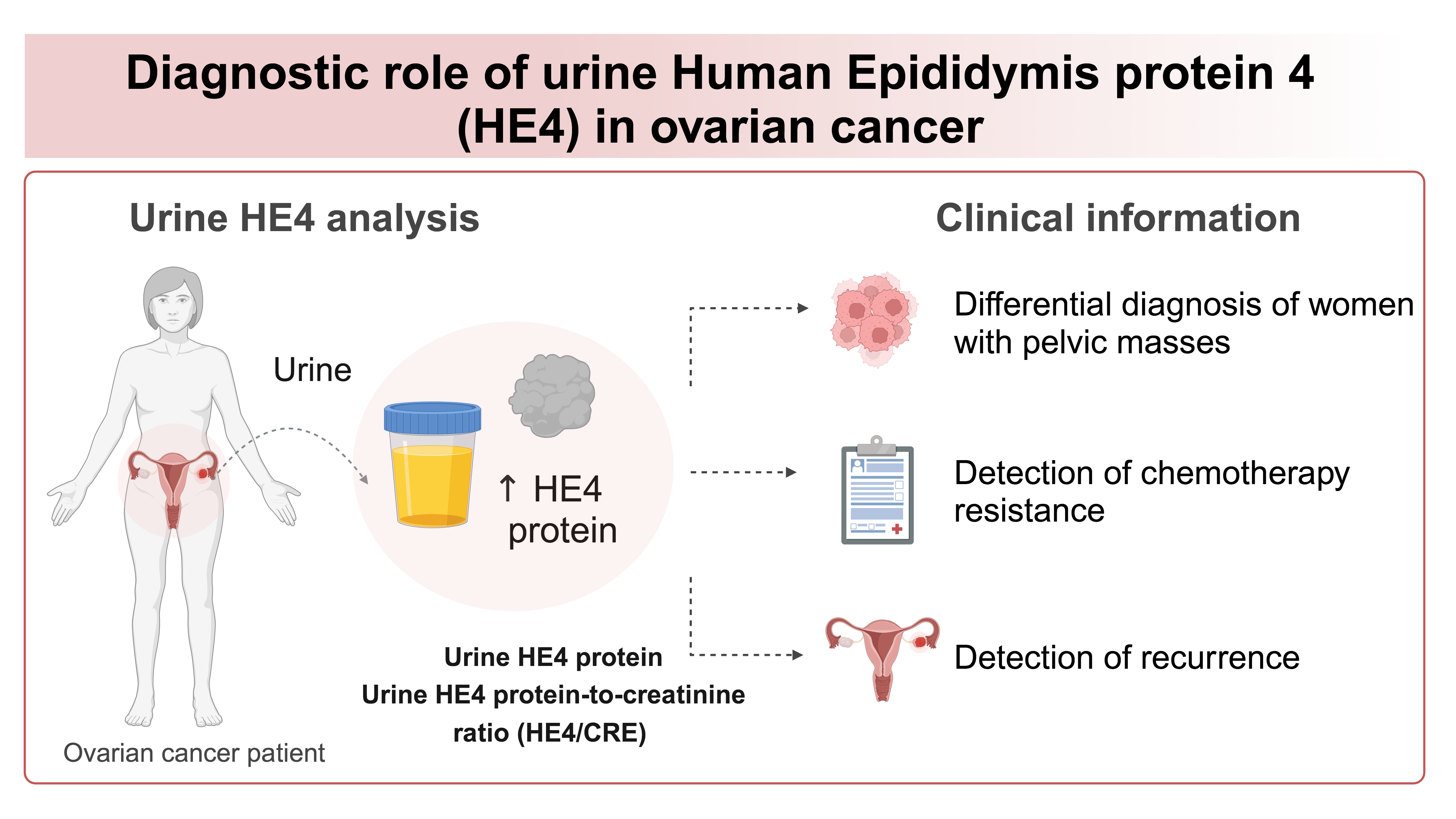
• Urine human epididymis protein 4 (HE4) and protein-to-creatinine ratio (HE4/CRE) are higher in ovarian cancer
• Urine HE4 and HE4/CRE ratio can be used in the differential diagnosis of ovarian cancer
• Urine HE4/CRE is a predictive marker of chemotherapy resistance and disease recurrence
• Urine HE4 can be detected in urine by immunoassays or mass spectrometry
• Standardization of the urine HE4 determination is needed before its clinical application
Ovarian cancer is the 8th most common malignancy in women and the deadliest gynecological cancer. Due to the non-specific symptoms and the lack of effective diagnostic methods, late diagnosis remains the main barrier for improving the poor prognosis. Human epididymis protein 4 (HE4) is a protein overexpressed in ovarian cancer, but not in healthy individuals or benign conditions. The aim of this review article is to evaluate the laboratory aspect and potential clinical application of urine HE4. The methodology is presented, together with discussion on preanalytical, analytical and postanalytical phase of HE4 detection using urine. Moreover, we present the diagnostic role of urine HE4 in differential diagnosis, chemotherapy response, detection of recurrence and detection of low-malignant potential tumors. It has been found that urine HE4 presents as a promising, non-invasive tumor marker for detection and monitoring of ovarian cancer. However, standardization of the HE4 detection process is needed prior to implementation in clinical diagnostics.
Keywords: epididymis-specific protein E4; human; ovarian cancer; tumor markers; urine; diagnosis