Journal Information
Journal ID (publisher-id): BM
Journal ID (nlm-ta): Biochem Med (Zagreb)
Title: Biochemia Medica
Abbreviated Title: Biochem. Med. (Zagreb)
ISSN (print): 1330-0962
ISSN (electronic): 1846-7482
Publisher: Croatian Society of Medical Biochemistry and Laboratory Medicine
Article Information
Copyright statement: Copyright Croatian Society of Medical Biochemistry and Laboratory Medicine
Copyright: 2024, Copyright Croatian Society of Medical Biochemistry and Laboratory Medicine
License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/):
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) 4.0 License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Date received: 02 January 2024
Date accepted: 08 March 2024
Publication date: 15 June 2024
Publication date: 15 June 2024
Volume: 34
Issue: 2
Electronic Location Identifier: 020501
Publisher ID: bm-34-2-020501
DOI: 10.11613/BM.2024.020501
Preanalytical, analytical and postanalytical considerations in circulating microRNAs measurement
Author notes:
[*] Corresponding author: zenmustapha@gmail.com
Author contributions
M Zendjabil: conceptualization, visualization, writing - original draft, review, editing.
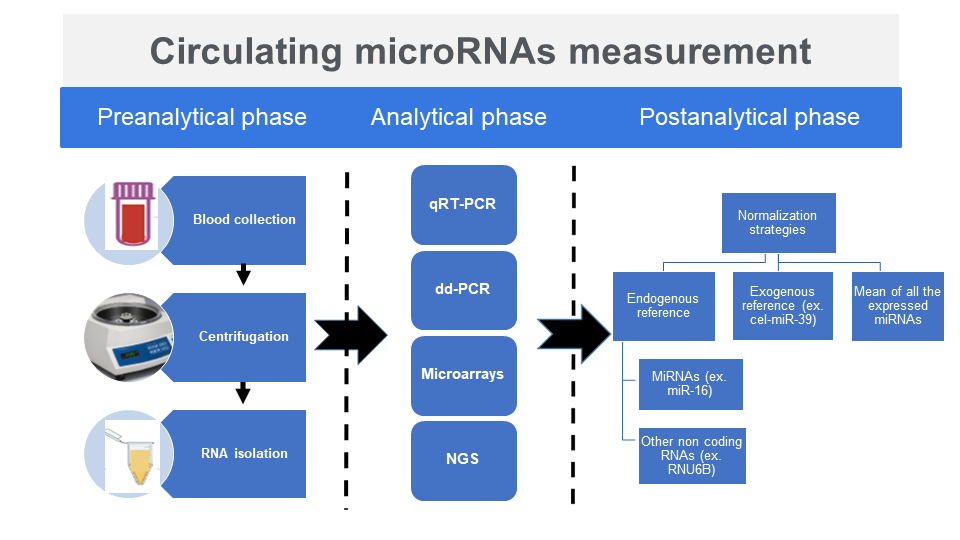
• Methods used for miRNAs expression profiling are quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction, microarrays, next generation sequencing and droplet digital PCR
• To obtain reproducible and accurate miRNAs expression profiling detection, it is crucial to strictly standardize the entire process, starting from choosing the specimen type until the normalization strategy on the interpretation of miRNAs expression profiling detection
•Due to the critical impact of the normalization strategy on the miRNAs expression, the choice of normalization agent is of great importance
Microribonucleic acids (miRNAs) have emerged as a new category of biomarkers for many human diseases like cancer, cardiovascular and neurodegenerative disorders. MicroRNAs can be detected in various body fluids including blood, urine and cerebrospinal fluid. However, the literature contains conflicting results for circulating miRNAs, which is the main barrier to using miRNAs as non-invasive biomarkers. This variability in results is largely due to differences between studies in sample processing methodology, miRNA quantification and result normalization. The purpose of this review is to describe the various preanalytical, analytical and postanalytical factors that can impact miRNA detection accuracy and to propose recommendations for the standardization of circulating miRNAs measurement.
Keywords: microRNAs; preanalytical phase; blood collection; biomarkers; liquid biopsy